Are you in search of a rotary dryer to take your business to the next level? Look no further! Here, we have all the information you need to make an informed decision. From understanding the advantages and disadvantages of rotary dryers to finding the best price on the market, we are here to help you make the most of your investment. You deserve a rotary drum dryer that fits your business needs and that’s exactly what we strive to deliver. We understand the importance of making wise choices when it comes to your business, and we are committed to helping you make the best one. So, let’s get started on this exciting journey of taking your business to new heights!
What is a Rotary Dryer?
A rotary dryer is an industrial machine meant to minimize or reduce the moisture of raw materials before they are processed in a pellet mill or similar type of machinery.
Rotary dryers can be used in all kinds of industries, including wood and animal feed pellets. They can even be used to dry stone, sand, soil, ore, grains, cereals, coffee beans, and many other types of materials.
These pieces of machinery can be used for just about any type of job, big or small. There are all kinds of different sizes, shapes, and designs to accommodate different types of products, different quantities, and different moisture content ranges.

Rotary Drum Dryer Working Principle, Design, Diagram
Many different rotary dryer designs can be used for different applications. The gas flow, drum design, and heat source affect the suitability of a machine for different types of materials.
Rotary Dryer Working Principle
The rotary dryer working principle sounds complicated but is actually quite straightforward.
The final product will have the proper moisture content and be discharged from the rotary drum dryer, allowing it to then be used in a pellet mill or any other type of finishing equipment, based on your business. If there is any fine powder, it will be collected by the dust collector to reduce the risk of messes and fire hazards. Purified gas that’s left behind will be dispersed into the air.
Here’s a quick tutorial:
- You’ll gather raw materials to be processed in the dryer, generally wood, before it is meant to go into the pellet mill or pellet machine.
- When the materials are ready to be dried, you’ll put them into the dry zone using special combination plates. These special plates are meant for drying via vertical movement. They are installed at varying angles based on the requirements and the rotational motion of the drying plate.
- The materials will be heated to high temperature, with a high-temperature furnace gas discharging into the system. This evaporates any existing water in the materials, drying them from the inside out. This unique design also prevents the material from sticking to the inside of the cylinder.
That’s the basic breakdown of how a rotary dryer works. A rotary dryer also has self-cleaning features. While it’s rotating, the inside wall is automatically cleaned, preventing the material from sticking to the wall.
Indirect Rotary Dryer /Direct Rotary Dryer
Beyond that, there are several different types of rotary dryers you can buy and various classifications.
They can usually be characterized as direct-heated rotary dryers, indirect-heated rotary dryers, or a special type, like a triple pass rotary drum dryer.
More often than not, the rotary dryers you will find for sale for your business can be classified as indirect rotary dryers or direct rotary dryers. We’ll break the technology for each of these down for you below.
In a direct-heated rotary dryer, the material comes into direct contact with the hot air. The hot air and materials all move in the same direction, even if the hot air temperature at the opening is higher.
Since the material still has surface moisture that needs to be evaporated, the temperature of the product remains the humidity temperature. This is known as a parallel current type of rotary dryer.
There’s also a counter-current type of rotary dryer, which is also direct-heated. In this system, as the name suggests, the airflow moves in the opposite direction of the material. This creates a significant temperature difference and is one of the best at transferring heat.
This kind of technology is often used for materials with high humidity and low combustibility, like sludge, and less often for wood pellet rotary dryers since wood is more combustible.
Rotary Dryer Design
A rotary dryer consists of the main body, a feeding system, a collector system, and a ducting system.
When the material enters the drum via the feeder, heat exchange between hot air and the material begins. The material moves along the bent plate on the drum wall through a rolling mechanism (hence the word “rotary”) and the introduced air. This is a concurrent flow drying technology, which is the most common technology used in rotary dryer design today.
The design of your rotary dryer will loosely follow the parameters specified above the “working principle” section.
However, there are some differences depending on the type of rotary dryer you buy and the individual machine’s design parameters.
Often, these design parameters are influenced by how much moisture needs to be taken out of the wood you will be processed into pellets. Some types, like sapwood, have much higher moisture than other types.
The amount of moisture that a dryer needs to remove can impact many aspects of the rotary dryer design. Other factors come into play for the various aspects of the dryer, too, and it is the interrelation of all of these factors together that determines the final design.
Here are some examples.
The retention time is a term used to describe the period of time that a raw material needs to stay within the dryer to reach the desired results. This impacts the overall size of the dryer and/or the dryer drum.
Another factor to consider is airflow. The moisture content of a raw material influences the airflow configuration of a dryer (or which direction the air flows in relative to the direction of the material co-current or counter-current).
Some materials carry a lot of moisture and require a fast initial dring. For materials like these, a co-current configuration is ideal because it makes the wet material come into contact with the hot drying gases first.
Both the length and diameter of the drum, relative to the rotary dryer’s design, can be influenced by a variety of intermingling factors, too. The airflow velocity that is required along with the retention time that is needed is both important in evaluating and determining the ideal rotary drum length, diameter, and design in this regard.
There are a few other factors that can differ in the design.
Heat Source
Gas streams are typically heated with burners using either coal or gas or sometimes oil. It can be made up of a mixture of combustion and air gases from a burner, in which case it is directly heated.
Instead, it can contain air and another preheated and often inert gas. This is an indirect-heated rotary dryer.
Drum Design
A rotary dryer can have one shell or multiple concentric shells (typically no more than three).
Having numerous drums can reduce the space that the equipment needs to get the same output.
Combined Processes
Sometimes, rotary dryers can combine other processes with drying, like cleaning, cooling, separating, and shredding. This can increase your efficiency and maximize your profits.
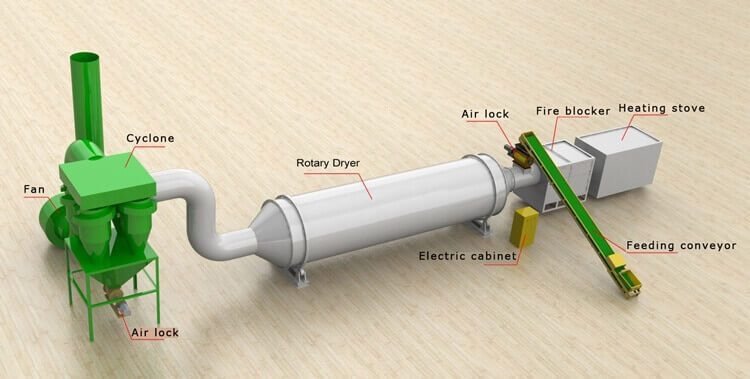
Rotary Dryer Diagram
If you need a visual depiction of how a rotary dryer works, don’t worry – there are plenty to be found online. These diagrams can make it easier to understand precisely how these kinds of machinery operate.
Below is a diagram that shows more detail on how a rotary dryer actually works.
What Does a Rotary Dryer Do? (Application)
Simply put, rotary dryers solve a common problem that exists when making pellets, and that is this: organic materials in their raw, unprocessed state simply have too much water to be useful in an industrial setting.
A rotary dryer gets rid of the excess water – it’s as simple as that. Of course, manually drying material or using some other type of equipment to dry it is another option to get rid of extra moisture, but it can be expensive, time-consuming, and ineffective.
Using a rotary dryer lets, you save space, save money, and save energy.
Rotary dryers are applicable in just about every industry. In fact, if you are new to understanding how rotary dryers work, you might be surprised to hear that you use a basic version of a rotary dryer in your own home – your clothes dryer! This common household appliance uses the same type of technology as an industrial rotary dryer, just on a smaller scale.
That’s not all, though. Rotary dryers are most popular in the forestry and biomass industries (hence, why we sell them along with other types of wood pellet production materials) as well as in other industries, such as ethanol, food production, livestock feed, pharmaceutical, sugar processing, and more.
There’s even a push for microbrewers to use rotary dryers and for users of rotary dryers everywhere to take advantage of new technology, torrefaction on an industrial scale.
How Much Does a Rotary Dryer Cost?
Rotary dryers can be used to dry all kinds of materials, from a chemical rotary dryer to a biomass rotary dryer biomass and everything in between. Because of this, there tends to be quite a lot of variability in their overall costs. A biomass rotary dryer will tend to be slightly less expensive than a chemical dryer, though that’s certainly not always the case.
You may find inexpensive home rotary dryers for just a few hundred dollars. On the other hand, there are some centrifugal-style rotary dryers that cost several thousand dollars (even $30,000 or more).
Carefully consider your required specifications and needs before you buy. Often, you don’t need to spend quite as much money as you might think!
Rotary Dryer Advantages and Disadvantages
Rotary dryers pose many advantages to business owners, larger and small.
For one, they can be used on many different types of products (most notably, wood products). Unlike other types of drying machinery, rotary dryers can be used on solid particles that aren’t uniform as well as those that are more uniform inconsistency.
They can also accept the hottest exhaust gases of any type of dryer. They aren’t as sensitive to particle size, as mentioned, and they have lower maintenance costs and a greater capacity.
Of course, you do have to make sure you choose the right type of rotary dryer to handle the material that you’re attempting to process.
The greatest benefit of a rotary dryer, therefore, is its ability to accommodate products with multiple and differently-sized particles and moisture contents. It keeps larger pieces in the drum longer while allowing slower pieces to exit more rapidly. Because of this, you’ll have more uniform output in your product moisture.
A rotary dryer can be used on any kind of project, large or small. These revolutionary machines come in all different quantities, product types, and moisture content ranges. A 14′ diameter drum is perfect for many people, but there are also larger drums available to accommodate various needs.
They can withstand high temperatures and corrosive materials, making them some of the toughest pieces of machinery you’ll have in your entire operation.
Rotary dryers are affordable, versatile, and economical.
Of course, as with anything, there are disadvantages to be noted, too. Fortunately, with rotary dryers, they are few and far between.
You may find that the drying process of super wet biomass in a rotary dryer is more challenging. That’s because it takes more time for uniform drying without increasing the risk of a fire hazard (smaller loads at one time may be necessary).
They can be costly if you’re only producing pellets on a small scale, and it can sometimes be tough to find a rotary dryer you need locally. Luckily for you, HENGMU has the perfect rotary dryer for your business – and it ships!


What Size Rotary Dryer Do I Need?
There are many different sizes and types of rotary dryers you can buy.
Generally, options range from units that are around eight tons to more than 118 tons. Obviously, those that are higher in tonnage have greater overall power and higher output. They generally can handle a higher capacity and may have a higher rate of speed.
Therefore, the more volume your business handles on a regular basis, the larger rotary dryer you will need. Consider one that has an internal diameter of 1800 mm or higher and a length of 22000 mm or larger for bigger volumes.
When deciding on the ideal rotary dryer, it is often more important to consider drying capacity and evaporation rates than it is size. Though these measurements often go hand in hand, it is the capacity you want to consider and not necessarily the size itself.
Again, rotary dryer efficiency is often part and parcel of its size, but consider its benefits in other areas in addition to just the amount of space it will take up in your workshop.
How to Buy an Affordable Rotary Dryer (Rotary Dryer Manufacturers)?
There are plenty of affordable rotary dryers out there – it is all about knowing what to look for.
Evaporation Rates
Evaporation rates vary among rotary dryers. Most can handle anywhere between 1,000 and 60,000 lbs of water evaporation per hour.
One of the biggest factors you need to consider when shopping for a rotary dryer – and one that will influence the price of your machine – is how hot it gets. Consider the temperature carefully. This can play a role in the type of material you are able to dry.
For fresh green crops, like alfalfa, you will need higher temperatures of up to 850C. The moisture content of the biomass you are inputting is around 50%.
If you are planning on drying material with less moisture, you can get away with a much lower drum temperature. This can be used for most non-fibrous materials that don’t remain as wet, like forest residues. These burn easier and don’t need temperatures that are quite as high because the evaporation rates don’t need to be as rapid.
Drying Systems
Drying systems can rely on several different types of mechanisms, including those that are gas, solid fuel, or liquid fired.
Pollution Prevention Systems
The best rotary dryers will also have pollution prevention systems in place. These can add to the overall cost of the rotary dryer but, in many cases, are necessary as dictated by local or federal regulations and standards.
These systems are meant to control things like odors along with contaminants like SOx, NOx, VOCs, and particulates.
Find the Right Rotary Dryer Manufacturers
Of course, you also need to dedicate some time to find the right rotary dryer manufacturer. Look for a company that adheres to the strictest quality management systems (such as ISO9001) and has strong standards for product design and manufacturing processes.
You want a company that removes any hidden dangers from your product – you don’t want anyone getting hurt on the job.
Finding rotary dryer manufacturers that ensure great customer service is also essential. There is nothing more frustrating than spending thousands of dollars on a rotary dryer only to find that they don’t actually pay attention to what their customers need.
Companies like HENGMU pride themselves on their craftsmanship along with their attention to their customers’ needs. We will go through extensive pre-and post-order checks, making sure your order is packaged and transported to perfection. We’ll make sure equipment is delivered without damage and, as needed, also help with installation and maintenance.

How to Operate a Biomass Rotary Dryer for Beginners?
As a beginner, it is important that you consult the individual instructions on your specific rotary dryer unit to make sure you understand the operational and safety guidelines set forth by the manufacturer.
The vast majority of rotary dryers are direct-fired, allowing the drying air and material to come into direct contact with each other. However, for people processing very fine materials, an indirect-fired rotary dryer is more advantageous.
With this kind of system, the drum will be heated externally.
To use your rotary dryer, you’ll start up the machine and make sure all parts are lubricated and in good working order. Feed the materials into one side of the dryer. They’ll come out the other side. Biomass materials with a higher water content will be fed into the cylinder, with hot air passing through the dryer to raise the internal temperature.
Your raw materials should absorb the heat, drying them and reducing their moisture from the inside out.
How to Improve the Rotary Dryer Efficiency?
There are a few ways to improve the efficiency of your rotary dryer. Aside from inserting smaller pieces of material (you can chip pieces down or process them into sawdust before feeding them into your machine), here are a few other tips to help you get more out of your rotary dryer.
For one, increase the temperature of the drying media inside the drying equipment. You can also increase the flow speed of the media since this is an adjustable feature on many models.
You can also reduce the feeding granularity or feed smaller amounts at once, which will allow the material to dry faster.
Another option is to shop for a rotary dryer that has multiple concentric shells instead of just one. Having multiple drums will reduce the amount of space and time you need to get these same outputs of dried materials.
With a legacy steeped in excellence, our extensive history in manufacturing high-quality rotary dryers is a testament to our unparalleled expertise. Over the years, we have meticulously refined our craft, positioning ourselves as industry leaders in the art of producing exceptional rotary dryer machines.
Three defining attributes of our high-quality rotary dryer machines are:
- Precision Engineering: Our rotary dryers are the result of meticulous design and engineering, where each component is thoughtfully crafted to ensure optimal performance and longevity. We integrate cutting-edge technology with time-tested principles to create machines that excel in efficiency and reliability.
- Superior Materials: Quality is at the core of our manufacturing process. We source and utilize the finest materials to construct rotary dryer machines that withstand rigorous operational demands. This commitment to using top-grade materials ensures durability, even in the most demanding industrial settings.
- Performance Excellence: Our rotary dryer machines are renowned for their exceptional performance. They exhibit impeccable drying efficiency, uniform results, and the ability to handle diverse feedstock with ease. This is a direct reflection of our rich experience, honed through years of perfecting the intricacies of dryer design and operation.
When you choose our rotary dryer machines, you’re choosing the culmination of our extensive experience, dedication to quality, and an unwavering commitment to delivering excellence in every aspect.

